share this post on
This article is part of our Prevention Tech in Insurance Whitepaper

for prevention tech in insurance
in prevention tech
in prevention tech
In today's digital age, the insurance industry is constantly evolving to keep pace with technological advancements and changing customer expectations. One significant development in this sector is the rapid emergence of prevention technology and services.
By utilizing innovative solutions such as sensors, data analytics, and artificial intelligence, insurers can now proactively identify and mitigate risks before they occur. This not only benefits customers by reducing the likelihood of claims but also presents a significant opportunity for insurers to improve profitability and customer retention.
In this article, we will delve into the business case and mechanisms of prevention technology in insurance while exploring the critical role played by IoT sensors and behavior design.
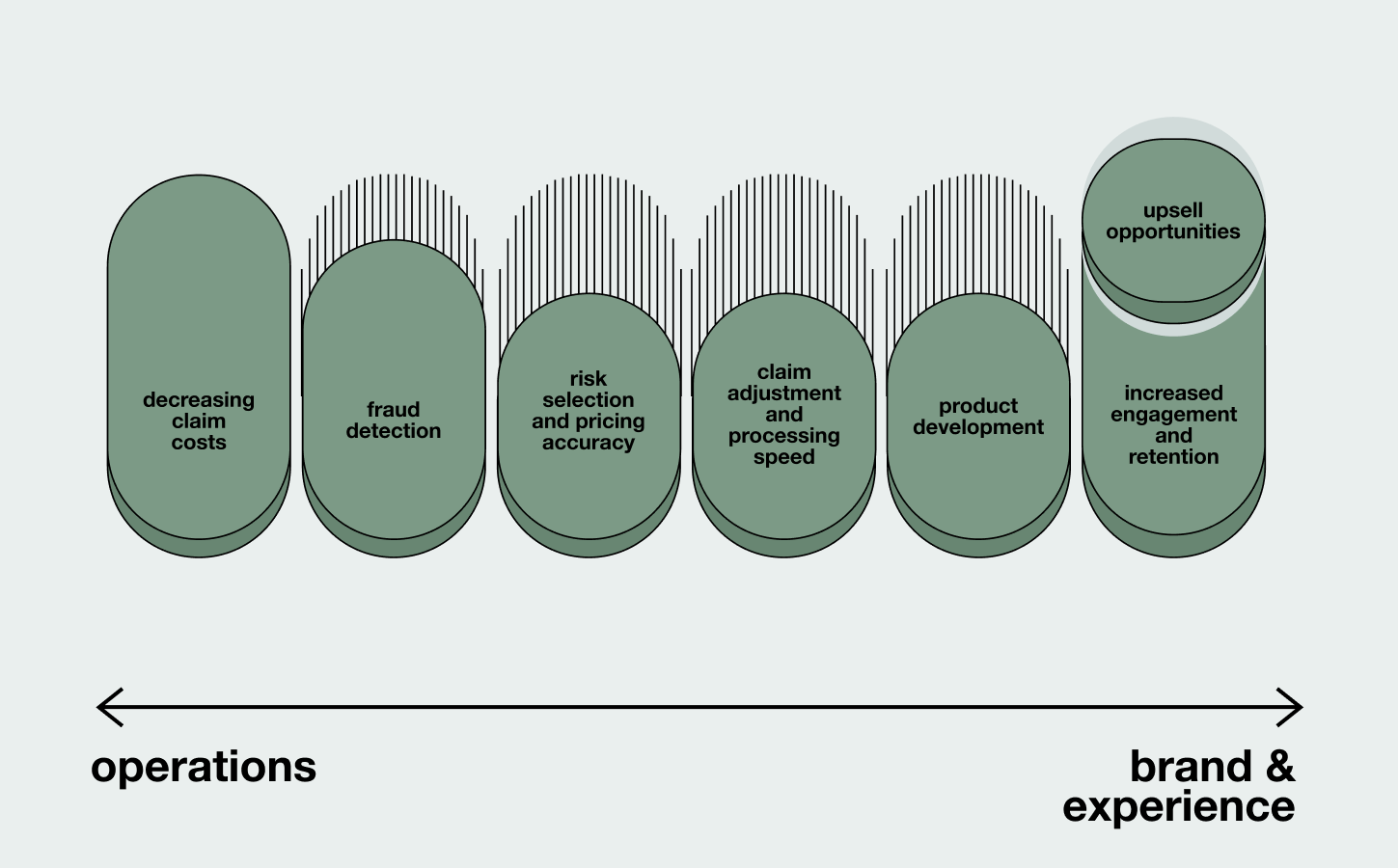
Preventing harm isn’t just driven by goodwill. Insurers can benefit greatly by developing digital products that help customers manage risks. Let's review some common goals that insurers have when utilizing prevention tech.
A sure way for any insurer to increase profitability is to decrease costs. Prevention technology can help avoid or minimize damages, lowering risks and improving loss ratios for a more profitable business. Alternatively, carriers can pass savings onto their customers through lower premiums, driving acquisition and retention.
However, there is a catch. The industry is still learning about the viability of prevention tech scenarios. Solutions can carry high development costs or licensing expenses and often require distributing expensive IoT devices. Despite this, the potential benefits of prevention technology should not be overlooked.
As prevention programs become more sophisticated and device costs decrease with advancing technology, the economics will become increasingly advantageous. It is also important to consider all business case aspects rather than focusing solely on claims costs and expenses.
Prevention tech lets insurers tap into rich and accurate data in real time from connected devices. This data can make risk and pricing models more accurate, and support claims management processes. One caveat - this isn’t out-of-the-box functionality. To unlock the power of connected devices, carriers must prioritize data transformation to build a direct, relevant picture of customer behavior in an insurance context.
We all know carriers want more engagement with customers. Insurance has typically struggled with customer experience; interactions with carriers only happen at onboarding, occasionally when checking policy details, and when making a claim - which most customers won’t do during the relationship. These are just too few touchpoints to enable participation in the experience economy and build any emotional connection with the customer.
Convenient self service experiences make life easier but don’t create additional reasons to engage. This leaves carriers competing on coverage, price point, and the strength of distribution networks. By embracing the new role of protection and actively protecting risks, the insurance experience changes instantly.
For example, Allstate claims that 30% of participants in their Drivewise program open their app at least once a month. Done right, this can create strong brand engagement and increase the length of the customer relationship.
With all the automatically incoming data, insurers can radically speed up the processing of claims and even proactively reach out to customers to start the FNOL (First Notice of Loss) process. If the data collection is meaningfully connected with process automation, this doesn’t just lead to a better customer experience but can also drive substantial savings on claim expenses.
Increasing touchpoints and engagement also increases attention, allowing carriers to upsell additional coverage. Note – this might require inventing new offers that work in the customers’ particular context.
The evolution of prevention tech will naturally invite carriers to create new offerings - whether innovating upon core insurance solutions (like usage-based insurance) or creating net-new, insurance-adjacent value add experiences (like safe driving instruction or password managers)
The prevention tech solutions we analyzed contain two essential components:
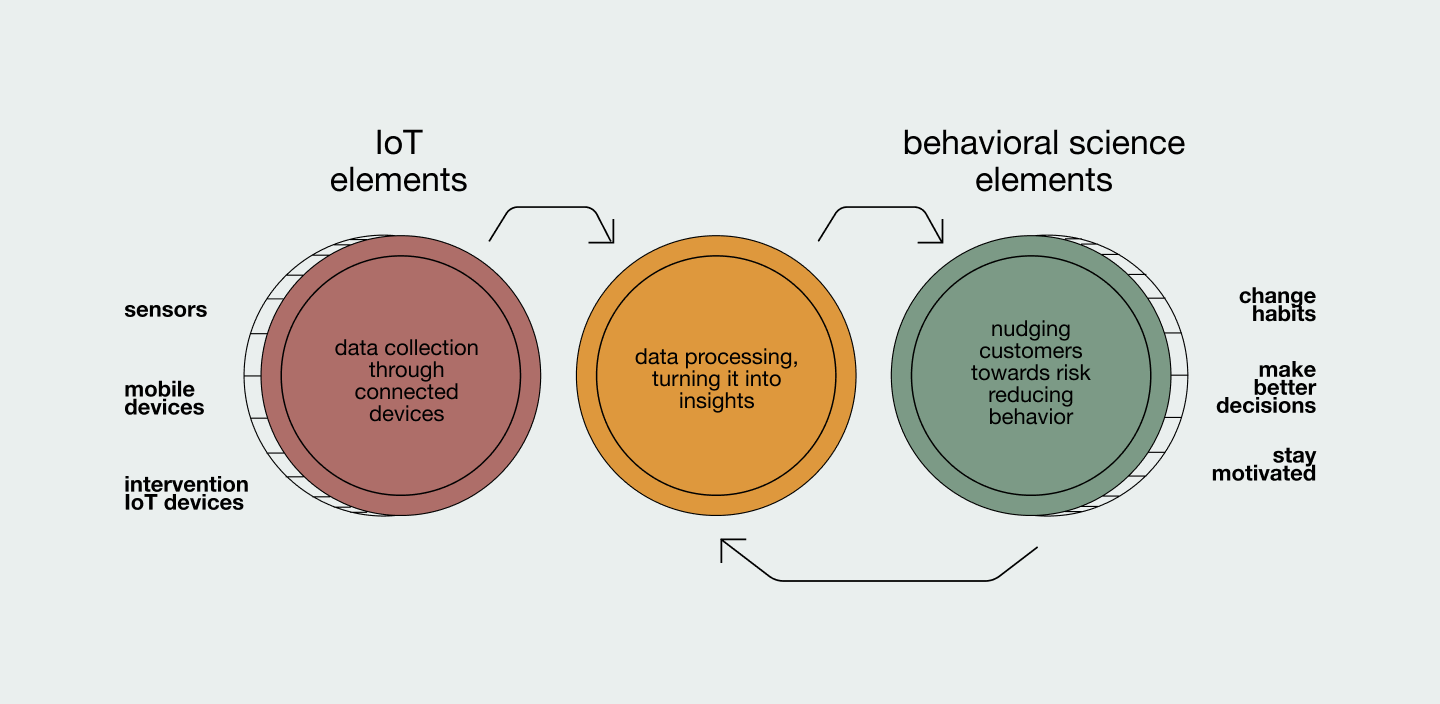
Providers use these two to varying degrees, but in general, most products begin by focusing on the IoT component and start adding behavior-influencing elements in later product stages.
There are now over 14 billion connected devices in the world, and they are rapidly entering every aspect of our lives. These devices are evolving from simple connected sensors to intelligent machines that can communicate with humans and directly affect their environment (think of shut-off valves or automatic braking.)
With the advancement of cloud computing, even the simplest connected device can display remarkable intelligence as complex calculations are running on powerful backends. These backends increasingly utilize Machine Learning based solutions – a technology that rapidly starts to show its real world utility advancing with a break-neck pace (if you need convincing, play around with ChatGPT or Midjourney for a few minutes).
While smart devices already impact everyday life, their true power is realized when they are connected to a meaningful ecosystem. There are industry-wide initiatives to increase device interoperability to enable orchestrating sophisticated customer experiences, but these are still in their infancy.
Generally, devices only reliably work together within the ecosystem of their manufacturer. While it is theoretically possible to build a connected world where a smartwatch can wake you up, start your coffee machine, recommend suitable clothes based on the weather, and warm up your car seat, this kind of magic is not yet available to customers.
Large players like Amazon, Apple and Google work hard to make their devices the epicenter of a user’s connected world through sophisticated voice interfaces (Alexa, Siri, Google Assistant), but they still have a long way to go to offer coherent, synergistic customer journeys across devices from different manufacturers.
However, with so much interest and investment in IoT, we expect rapid evolution in the coming years.
The lack of complete orchestrators allows insurers to play a unique role in a connected device ecosystem. When property and casualty insurers think about using connected devices for prevention, it can be helpful to consider the following categorization.
These elements can be divided into three layers: the device layer, the data processing layer, and the service layer.
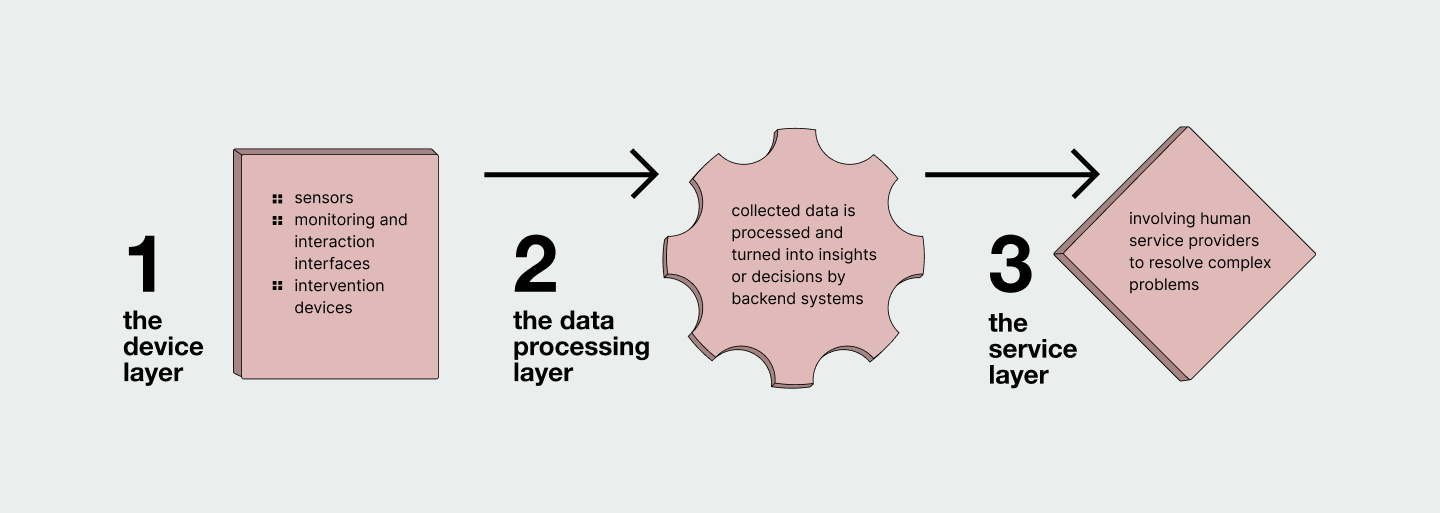
By understanding the different components that make up a prevention experience, insurers can identify the specific elements they want to incorporate into their strategy and optimize their use of connected devices for prevention.
It's worth noting that one device can play multiple roles. While smartphones are generally not classified as IoT devices, it is practical to treat them as such - as in Usage-Based Car Insurance, where the phone plays the role of the sensor besides also being the reporting area.
In modern architectures, business logic is typically delegated to a cloud-based backend, meaning that smart devices are not intelligent on their own - “thinking" happens on servers located remotely. The data collected by smart devices is processed and turned into insights or decisions by the backend system, primarily by device manufacturers who use it to deliver essential functionality.
Typically, this is where insurers who want to build their own prevention tech solutions can join in: accessing the data through APIs offered by the device manufacturer.
While many carriers have chosen to leave the tech side to IoT partners, the future may require insurance companies to follow the lead of the banking industry and invest in their own digital product innovation to enhance digital capabilities, expertise, and intellectual property.
Direct access to the vast amount of data generated by IoT devices will be essential for this, as the insurance industry was always built on data from its inception hundreds of years ago.
By embracing digital innovation and leveraging data, insurers can stay competitive in the rapidly-evolving digital landscape.
By accessing data from connected devices, insurers can create or participate in complex ecosystems that bring previously disconnected devices together for improved prevention outcomes.
This data can help insurers assist their customers in making better decisions to avoid risk and enable completely personalized offers through more accurate risk and pricing calculations.
Insurance companies can create the most value for their customers by combining smart devices with human services. While smart devices are effective at identifying issues, they are limited in their ability to handle complex mitigation tasks.
By involving human service providers, insurers can offer a comprehensive solution that not only detects problems but also resolves them. Combining technology and human expertise is the key to creating customer value.
Some device manufacturers create their own service ecosystems. For example, Ting offers a remote fire safety team that guides customers through the mitigation process and can even dispatch a certified electrician for more complex tasks. Security system manufacturers generate much of their revenue through professional monitoring services: when an alarm is triggered, a human expert assesses the threat and takes necessary action, such as contacting the police.
However, most smart devices come without any service components, creating an excellent opportunity for insurance companies to add value and create cohesive offerings that solve complex customer needs. Smart devices can help insurers create value for their customers with targeted advice and support.
For example, sensors that recognize poor driving habits can send notifications to an app, providing helpful tips and guidance - but connecting customers with advanced driving instructors is an even more powerful tool for reducing driving-related risk. By offering professional, in-person support, insurers can significantly improve the driving skills of their customers and create a safer, more secure environment.
There is definitely a significant human element to preventing risk. If policyholders were better educated about possible prevention opportunities or prompted in the right context, many risks could be avoided or minimized.
This is why prevention tech solutions aim at influencing user behavior to help make better decisions. While this is an afterthought in many of today’s products, we expect to see more impactful solutions in the future that prioritize behavioral science.
Behavioral design involves creating experiences based on a systematic understanding of how people think and make decisions.
In the context of prevention, understanding evolutionary human biases and mental shortcuts helps designers create products and services that steer them toward safer habits and smart decisions that decrease risk.
Human biases toward risk-taking and risk avoidance are powerful and can lead us to make decisions not in our best interests. These biases are often based on outdated mental shortcuts developed to help our ancestors survive, which may not be relevant to our modern lives. Insurance companies can help us overcome these biases by offering prevention technologies designed to counter our misjudgements and help us make better decisions about risk.
The following list contains behavioral design techniques well-suited to different prevention tech applications. Varied use cases call for a different mix, but these elements should be part of a well-designed experience aiming to help customers to decrease risk.
The relationship between action and risk is not easily recognizable, or even worse; it's sometimes counterintuitive. The first step of any behavioral influencing program must involve educating users.
When it comes to auto insurance, the user might not have a clear understanding of what safe driving really entails or what level of sudden acceleration increases risk. A Florida homeowner who recently purchased their property might not understand the preventive actions needed for storms.
Educating users seems simple enough on the surface, but it’s a surprisingly hard design challenge, given how many things are competing for their attention today. Bite-sized knowledge delivered in an entertaining, easy-to-digest format at the right moment is the key to getting users to consume it.
Providing feedback is crucial for any activity where outcomes are measurable. Good feedback is delivered immediately after an attempt, is easy to discover and interpret, and includes relevant guidance on how to improve.
Insurers' usage-based insurance (UBI) applications often fall short in this regard, with generic feedback that is not delivered in a timely manner. An example of effective feedback is the Snapshot plug-in device, which beeps when a driver brakes too hard. This immediate feedback loop is minimally disruptive and gives users the information they need to improve their driving without overwhelming them with additional instructions.
Designing effective feedback that does not create additional risks by distraction is a challenging task, but it is essential for helping users improve and make better decisions.
“Nudging” customers is an established concept originally appearing in behavioral economics and policy making. It means designing a choice architecture - how a decision is laid out - so customers are likelier to opt for the beneficial alternative.
Insurers are more knowledgeable than customers on which behaviors will encourage safer outcomes, but customers are free to make their own choices - even risky ones. This is where nudges come into play: by leveraging behavioral science, we can make an option easier or more attractive.
For example behavioral science tells us stories that engage the human mind and make issues feel more personal, while statistics may be perceived as applying to others rather than the individual. Confronted with scary anecdotes or imagery of car accidents can motivate drivers to focus on safety more effectively than some alarming data.
Keeping users engaged and committed to their goals is one of the biggest challenges in behavioral design.
While most adults are willing to commit to goals that decrease their risk and increase their well-being, they often struggle to follow through due to conflicting priorities and the desire for immediate comfort or enjoyment. In theory, almost everyone agrees that complex and different passwords for different applications are smart decisions, but when it comes to setting them, they put in the same old password on every site.
To increase adherence to safer behaviors, companies can use various methods like relevant reminders, habit building loops, and gamification techniques tailored to audience needs and fit seamlessly within the context of a prevention application.
Most insurance companies' consumer-facing digital products pay little attention to motivation and do not go beyond simple gamification techniques. As these products mature, we expect insurers to start paying more attention to all elements of behavioral design to better engage and retain their users.
Prevention tech and data collection are inseparable. Data privacy needs to be a serious consideration when designing any prevention tech program.
According to a recent study involving 2500 homeowner’s insurance policyholders, 65% would be willing to share their data with their insurer in exchange for policy discounts but only 13% would do it without monetary incentives. In the same study, 62% said they are concerned about privacy when it comes to their insurer.
These figures and real life prevention tech participation numbers show that as long as consumer anxiety around data privacy is well addressed and the 'deal is right', these reservations are rarely insurmountable.
In industries where data privacy concerns are particularly prominent, such as banking, insurance, and healthcare, we have observed that while customers express concerns about privacy in surveys, their behavior does not always align with their stated sentiment.
We've seen this play out over 10+ years in delivering digital products for insurance and financial services companies. Deloitte’s 2021 research reinforces our observations, concluding that while data privacy issues dominate the discourse, it does not yet drive consumer decisions.
The best way to explore the real business value behind prevention in insurance is to dive into practical examples of real world leaders and what they are doing in their respective lines of business.
Download our whitepaper, and check out our benchmark of prevention tech in Auto, Property, Commercial and Cyber Insurance.